Code
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltWeek 4 sunspots data
('Sunspots.csv', <http.client.HTTPMessage at 0x291fef150>)def plot_series(x, y, format="-", start=0, end=None,
title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None ):
"""
Visualizes time series data
Args:
x (array of int) - contains values for the x-axis
y (array of int or tuple of arrays) - contains the values for the y-axis
format (string) - line style when plotting the graph
label (string) - tag for the line
start (int) - first time step to plot
end (int) - last time step to plot
title (string) - title of the plot
xlabel (string) - label for the x-axis
ylabel (string) - label for the y-axis
legend (list of strings) - legend for the plot
"""
# Setup dimensions of the graph figure
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Check if there are more than two series to plot
if type(y) is tuple:
# Loop over the y elements
for y_curr in y:
# Plot the x and current y values
plt.plot(x[start:end], y_curr[start:end], format)
else:
# Plot the x and y values
plt.plot(x[start:end], y[start:end], format)
# Label the x-axis
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
# Label the y-axis
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
# Set the legend
if legend:
plt.legend(legend)
# Set the title
plt.title(title)
# Overlay a grid on the graph
plt.grid(True)
# Draw the graph on screen
plt.show()| Unnamed: 0 | Date | Monthly Mean Total Sunspot Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1749-01-31 | 96.7 |
| 1 | 1 | 1749-02-28 | 104.3 |
| 2 | 2 | 1749-03-31 | 116.7 |
| 3 | 3 | 1749-04-30 | 92.8 |
| 4 | 4 | 1749-05-31 | 141.7 |
def windowed_dataset(series, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer):
"""Generates dataset windows
Args:
series (array of float) - contains the values of the time series
window_size (int) - the number of time steps to include in the feature
batch_size (int) - the batch size
shuffle_buffer(int) - buffer size to use for the shuffle method
Returns:
dataset (TF Dataset) - TF Dataset containing time windows
"""
# Generate a TF Dataset from the series values
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)
# Window the data but only take those with the specified size
dataset = dataset.window(window_size + 1, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)
# Flatten the windows by putting its elements in a single batch
dataset = dataset.flat_map(lambda window: window.batch(window_size + 1))
# Create tuples with features and labels
dataset = dataset.map(lambda window: (window[:-1], window[-1]))
# Shuffle the windows
dataset = dataset.shuffle(shuffle_buffer)
# Create batches of windows
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
return dataset# Reset states generated by Keras
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# Build the model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30, input_shape=[window_size], activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
# Print the model summary
model.summary()Model: "sequential"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ dense (Dense) │ (None, 30) │ 930 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_1 (Dense) │ (None, 10) │ 310 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_2 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 11 │ └─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 1,251 (4.89 KB)
Trainable params: 1,251 (4.89 KB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
# Set the learning rate scheduler
lr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(
lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))
# Initialize the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(), optimizer=optimizer)
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule],verbose=0)# Define the learning rate array
lrs = 1e-8 * (10 ** (np.arange(100) / 20))
# Set the figure size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Set the grid
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the loss in log scale
plt.semilogx(lrs, history.history["loss"])
# Increase the tickmarks size
plt.tick_params('both', length=10, width=1, which='both')
# Set the plot boundaries
plt.axis([1e-8, 1e-3, 0, 100])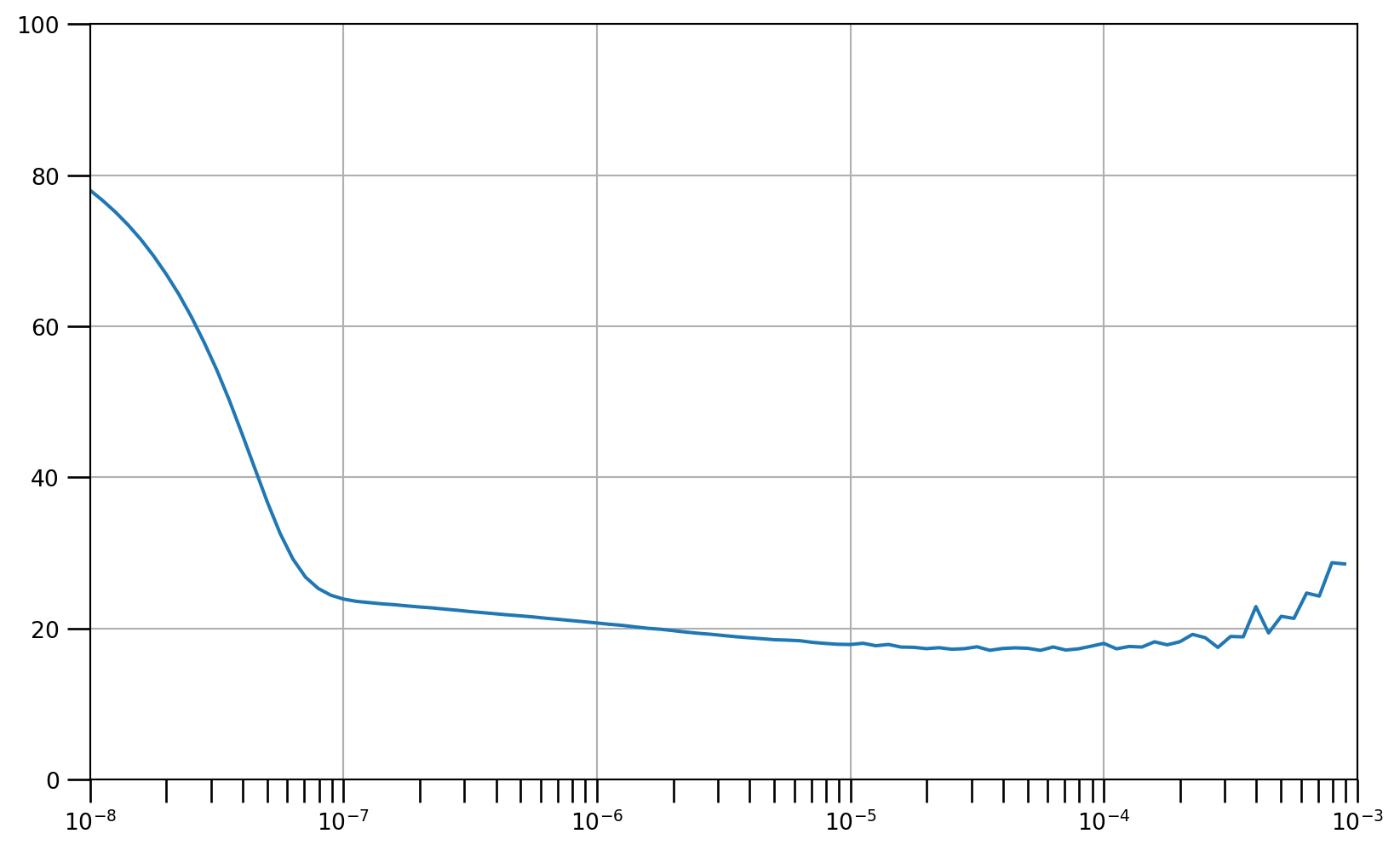
def model_forecast(model, series, window_size, batch_size):
"""Uses an input model to generate predictions on data windows
Args:
model (TF Keras Model) - model that accepts data windows
series (array of float) - contains the values of the time series
window_size (int) - the number of time steps to include in the window
batch_size (int) - the batch size
Returns:
forecast (numpy array) - array containing predictions
"""
# Generate a TF Dataset from the series values
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)
# Window the data but only take those with the specified size
dataset = dataset.window(window_size, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)
# Flatten the windows by putting its elements in a single batch
dataset = dataset.flat_map(lambda w: w.batch(window_size))
# Create batches of windows
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
# Get predictions on the entire dataset
forecast = model.predict(dataset)
return forecastforcast one value
1/Unknown 0s 18ms/step1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 19ms/step# Reduce the original series
forecast_series = series[split_time-window_size:-1]
# Use helper function to generate predictions
forecast = model_forecast(model, forecast_series, window_size, batch_size)
# Drop single dimensional axis
results = forecast.squeeze()
# Plot the results
plot_series(time_valid, (x_valid, results))WARNING:tensorflow:5 out of the last 18 calls to <function TensorFlowTrainer.make_predict_function.<locals>.one_step_on_data_distributed at 0x2a1cdb060> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has reduce_retracing=True option that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
1/Unknown 0s 19ms/step8/8 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step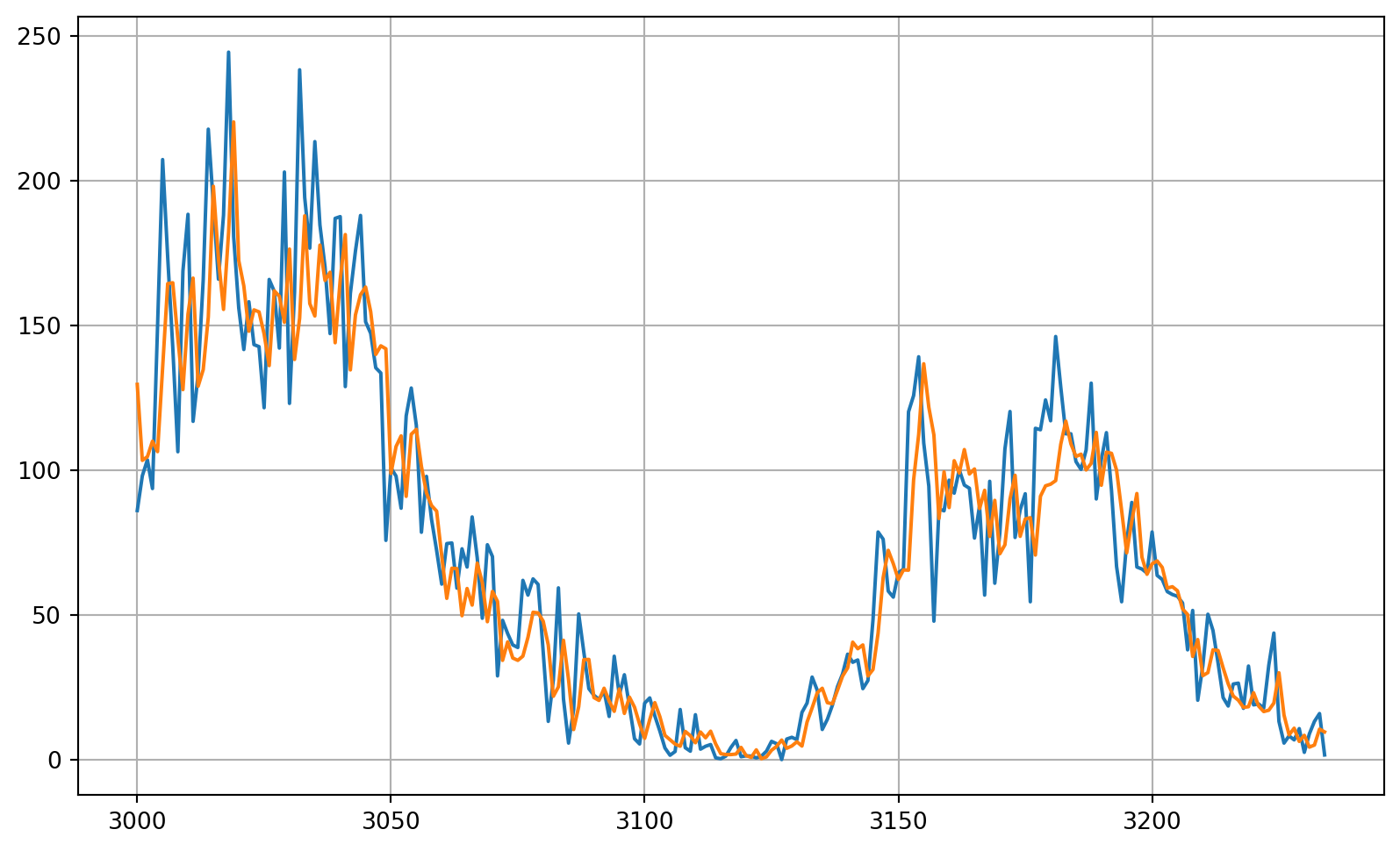
464.83243# Build the Model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv1D(filters=64, kernel_size=3,
strides=1,
activation="relu",
padding='causal',
input_shape=[window_size, 1]),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, return_sequences=True),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),
tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 400)
])
# Print the model summary
model.summary()Model: "sequential_1"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ conv1d (Conv1D) │ (None, 30, 64) │ 256 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lstm (LSTM) │ (None, 30, 64) │ 33,024 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lstm_1 (LSTM) │ (None, 64) │ 33,024 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_3 (Dense) │ (None, 30) │ 1,950 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_4 (Dense) │ (None, 10) │ 310 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_5 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 11 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lambda (Lambda) │ (None, 1) │ 0 │ └─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 68,575 (267.87 KB)
Trainable params: 68,575 (267.87 KB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
# Set the learning rate scheduler
lr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(
lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))
# Initialize the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(), optimizer=optimizer)
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule],verbose=0)# Define the learning rate array
lrs = 1e-8 * (10 ** (np.arange(100) / 20))
# Set the figure size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Set the grid
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the loss in log scale
plt.semilogx(lrs, history.history["loss"])
# Increase the tickmarks size
plt.tick_params('both', length=10, width=1, which='both')
# Set the plot boundaries
plt.axis([1e-8, 1e-3, 0, 100])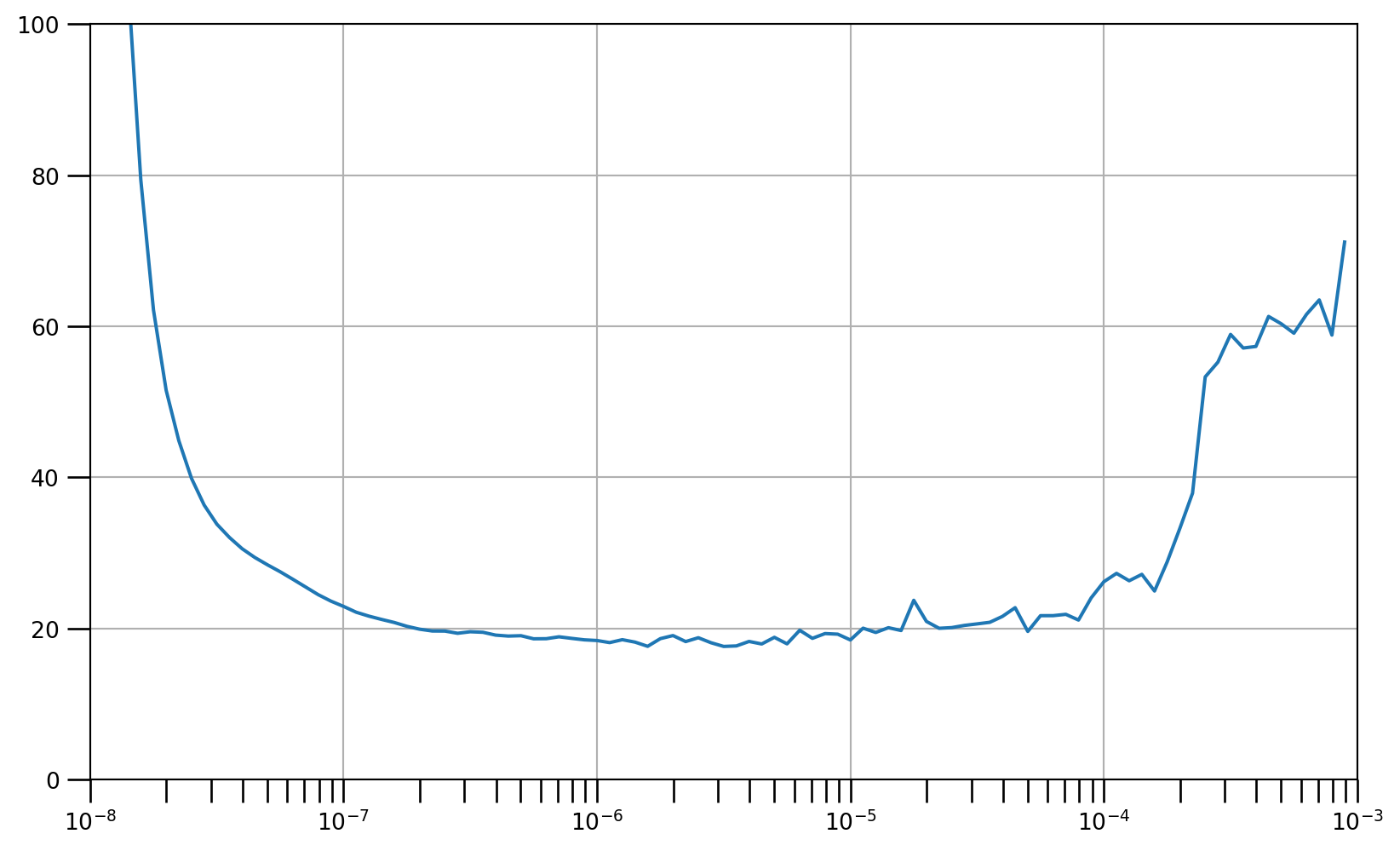
Model: "sequential_1"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ conv1d (Conv1D) │ (None, 30, 64) │ 256 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lstm (LSTM) │ (None, 30, 64) │ 33,024 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lstm_1 (LSTM) │ (None, 64) │ 33,024 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_3 (Dense) │ (None, 30) │ 1,950 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_4 (Dense) │ (None, 10) │ 310 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ dense_5 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 11 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ lambda (Lambda) │ (None, 1) │ 0 │ └─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 137,152 (535.75 KB)
Trainable params: 68,575 (267.87 KB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
Optimizer params: 68,577 (267.88 KB)
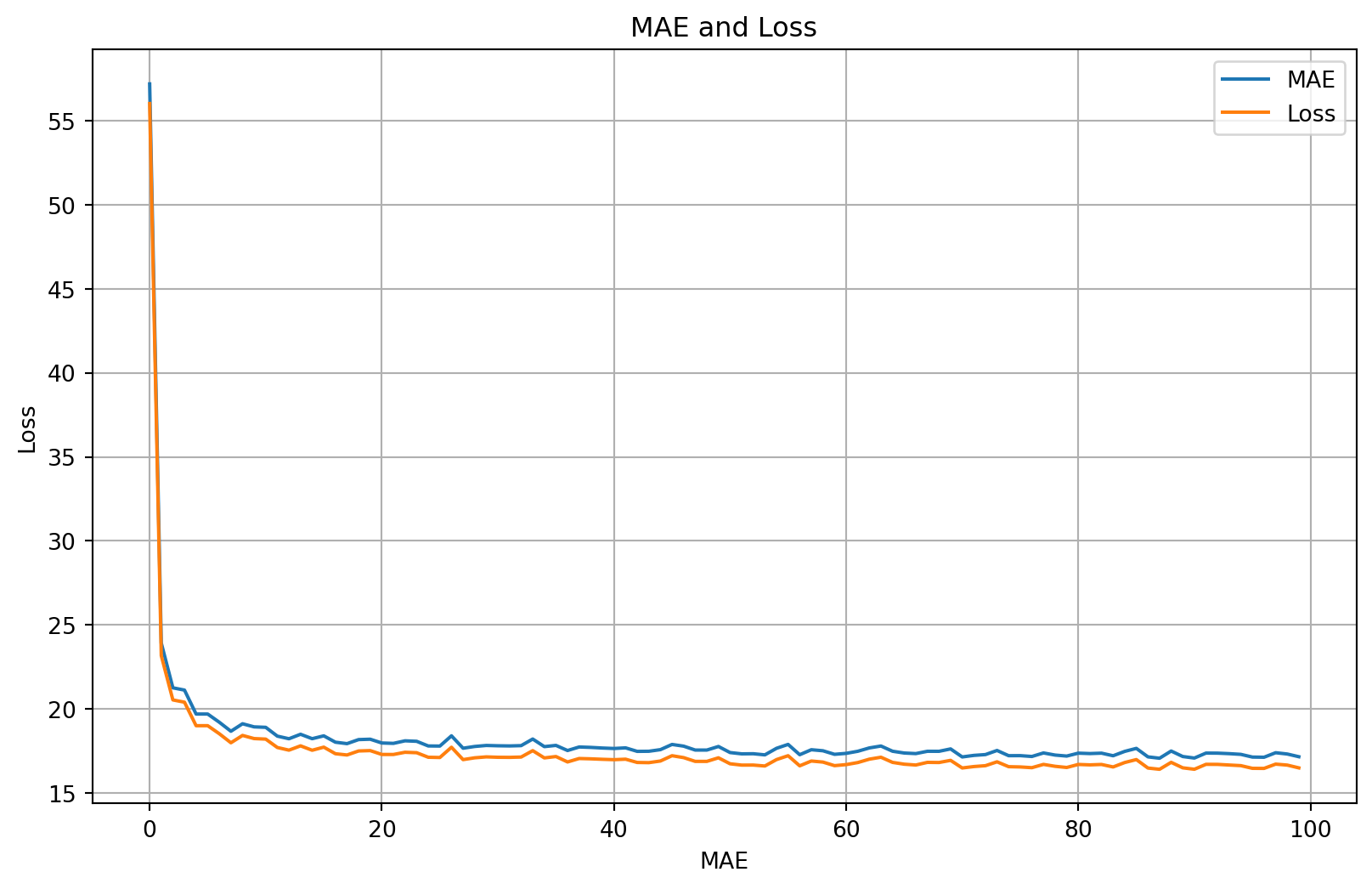
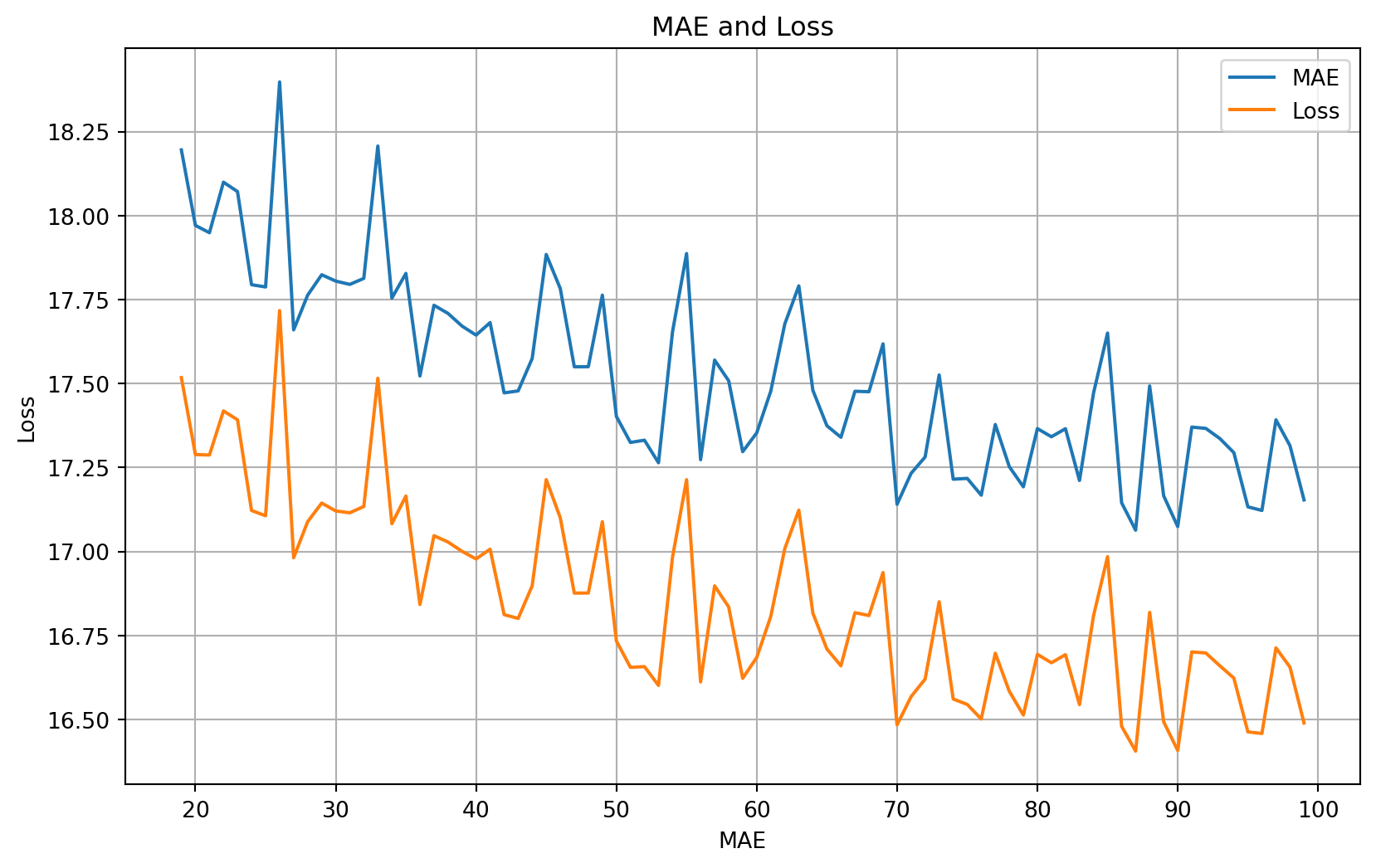
# Get mae and loss from history log
mae=history.history['mae']
loss=history.history['loss']
# Get number of epochs
epochs=range(len(loss))
# Plot mae and loss
plot_series(
x=epochs,
y=(mae, loss),
title='MAE and Loss',
xlabel='MAE',
ylabel='Loss',
legend=['MAE', 'Loss']
)
# Only plot the last 80% of the epochs
zoom_split = int(epochs[-1] * 0.2)
epochs_zoom = epochs[zoom_split:]
mae_zoom = mae[zoom_split:]
loss_zoom = loss[zoom_split:]
# Plot zoomed mae and loss
plot_series(
x=epochs_zoom,
y=(mae_zoom, loss_zoom),
title='MAE and Loss',
xlabel='MAE',
ylabel='Loss',
legend=['MAE', 'Loss']
)
# Reduce the original series
forecast_series = series[split_time-window_size:-1]
# Use helper function to generate predictions
forecast = model_forecast(model, forecast_series, window_size, batch_size)
# Drop single dimensional axis
results = forecast.squeeze()
# Plot the results
plot_series(time_valid, (x_valid, results)) 1/Unknown 0s 153ms/step 8/Unknown 0s 23ms/step 8/8 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step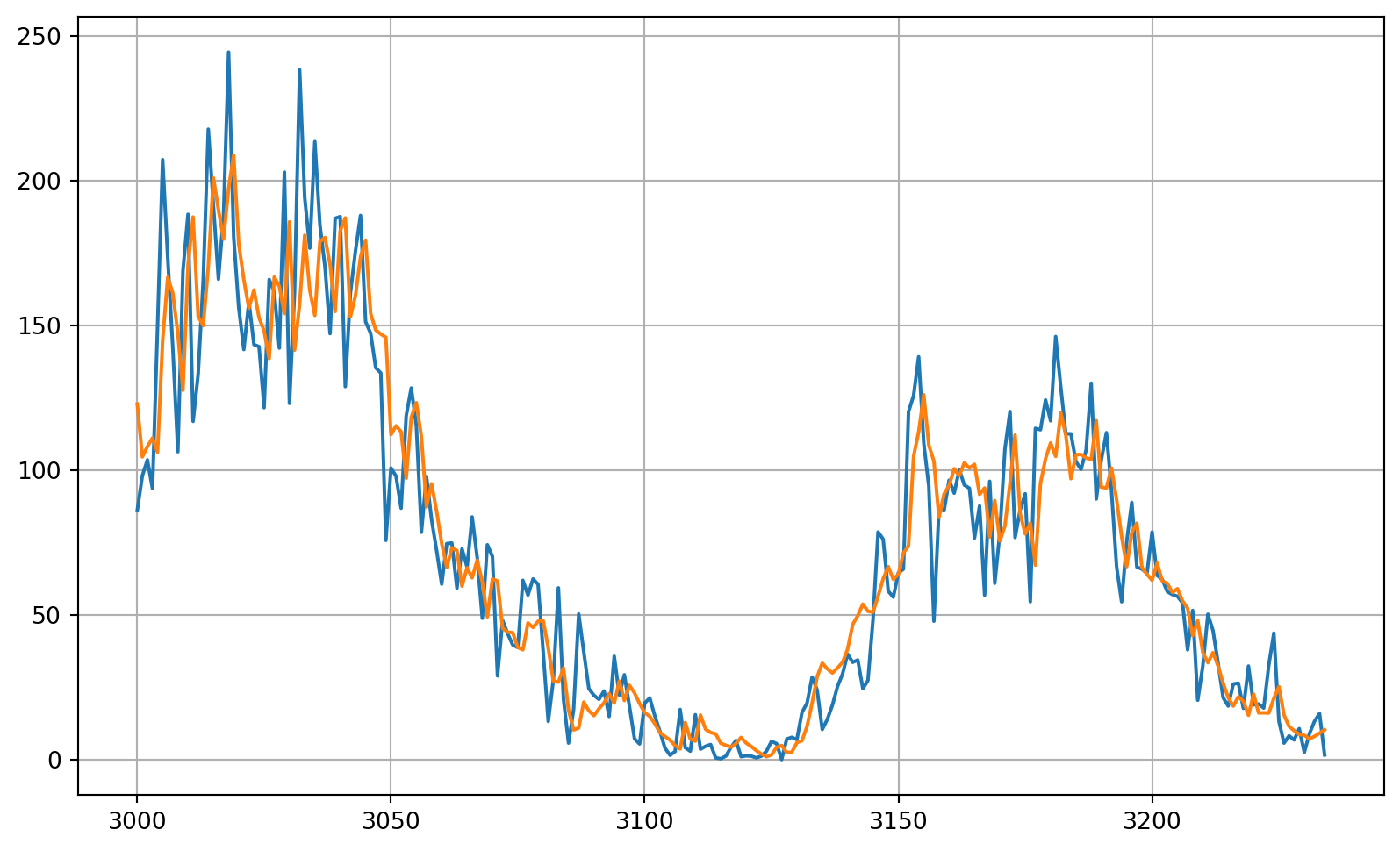
419.6377https://www.coursera.org/learn/tensorflow-sequences-time-series-and-prediction
https://github.com/https-deeplearning-ai/tensorflow-1-public/tree/main/C4
---
title: "W4:Real-world time series data sunspots"
execute:
warning: false
error: false
format:
html:
toc: true
toc-location: right
code-fold: show
code-tools: true
number-sections: true
code-block-bg: true
code-block-border-left: "#31BAE9"
---
Week 4 sunspots data
```{python}
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
```
# download data
```{python}
import urllib.request
url="https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow-1-public/course4/Sunspots.csv"
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, "Sunspots.csv")
```
```{python}
#| code-fold: true
#| code-summary: "Show the code"
def plot_series(x, y, format="-", start=0, end=None,
title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None ):
"""
Visualizes time series data
Args:
x (array of int) - contains values for the x-axis
y (array of int or tuple of arrays) - contains the values for the y-axis
format (string) - line style when plotting the graph
label (string) - tag for the line
start (int) - first time step to plot
end (int) - last time step to plot
title (string) - title of the plot
xlabel (string) - label for the x-axis
ylabel (string) - label for the y-axis
legend (list of strings) - legend for the plot
"""
# Setup dimensions of the graph figure
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Check if there are more than two series to plot
if type(y) is tuple:
# Loop over the y elements
for y_curr in y:
# Plot the x and current y values
plt.plot(x[start:end], y_curr[start:end], format)
else:
# Plot the x and y values
plt.plot(x[start:end], y[start:end], format)
# Label the x-axis
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
# Label the y-axis
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
# Set the legend
if legend:
plt.legend(legend)
# Set the title
plt.title(title)
# Overlay a grid on the graph
plt.grid(True)
# Draw the graph on screen
plt.show()
```
# read in data
```{python}
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv('./Sunspots.csv')
data.head()
```
```{python}
list(data)
```
```{python}
time=data['Unnamed: 0'].to_numpy()
```
```{python}
series=data["Monthly Mean Total Sunspot Number"].to_numpy()
```
# plot data
```{python}
# Preview the data
plot_series(time, series, xlabel='Month', ylabel='Monthly Mean Total Sunspot Number')
```
# Split the Dataset
```{python}
# Define the split time
split_time = 3000
# Get the train set
time_train = time[:split_time]
x_train = series[:split_time]
# Get the validation set
time_valid = time[split_time:]
x_valid = series[split_time:]
```
# Prepare Features and Labels
```{python}
#| code-fold: true
#| code-summary: "Show the code"
def windowed_dataset(series, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer):
"""Generates dataset windows
Args:
series (array of float) - contains the values of the time series
window_size (int) - the number of time steps to include in the feature
batch_size (int) - the batch size
shuffle_buffer(int) - buffer size to use for the shuffle method
Returns:
dataset (TF Dataset) - TF Dataset containing time windows
"""
# Generate a TF Dataset from the series values
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)
# Window the data but only take those with the specified size
dataset = dataset.window(window_size + 1, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)
# Flatten the windows by putting its elements in a single batch
dataset = dataset.flat_map(lambda window: window.batch(window_size + 1))
# Create tuples with features and labels
dataset = dataset.map(lambda window: (window[:-1], window[-1]))
# Shuffle the windows
dataset = dataset.shuffle(shuffle_buffer)
# Create batches of windows
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
return dataset
```
```{python}
# Parameters
window_size = 30
batch_size = 32
shuffle_buffer_size = 1000
# Generate the dataset windows
train_set = windowed_dataset(x_train, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer_size)
```
# DNN model
## define DNN Model
```{python}
# Reset states generated by Keras
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# Build the model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30, input_shape=[window_size], activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
# Print the model summary
model.summary()
```
## Tune the Learning Rate
```{python}
#| error: false
# Set the learning rate scheduler
lr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(
lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))
# Initialize the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(), optimizer=optimizer)
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule],verbose=0)
```
```{python}
# Define the learning rate array
lrs = 1e-8 * (10 ** (np.arange(100) / 20))
# Set the figure size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Set the grid
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the loss in log scale
plt.semilogx(lrs, history.history["loss"])
# Increase the tickmarks size
plt.tick_params('both', length=10, width=1, which='both')
# Set the plot boundaries
plt.axis([1e-8, 1e-3, 0, 100])
```
## define DNN Model after tunned
```{python}
# Reset states generated by Keras
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# Build the Model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30, input_shape=[window_size], activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
```
## complie model
```{python}
# Set the learning rate
learning_rate = 2e-5
# Set the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate, momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(),
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=["mae"])
```
## train DNN Model after tunned
```{python}
#| error: false
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set,epochs=100,verbose=0)
```
## Model Prediction
```{python}
#| code-fold: true
#| code-summary: "Show the code"
def model_forecast(model, series, window_size, batch_size):
"""Uses an input model to generate predictions on data windows
Args:
model (TF Keras Model) - model that accepts data windows
series (array of float) - contains the values of the time series
window_size (int) - the number of time steps to include in the window
batch_size (int) - the batch size
Returns:
forecast (numpy array) - array containing predictions
"""
# Generate a TF Dataset from the series values
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)
# Window the data but only take those with the specified size
dataset = dataset.window(window_size, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)
# Flatten the windows by putting its elements in a single batch
dataset = dataset.flat_map(lambda w: w.batch(window_size))
# Create batches of windows
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
# Get predictions on the entire dataset
forecast = model.predict(dataset)
return forecast
```
forcast one value
```{python}
forecast_series = series[split_time:split_time+window_size]
forecast = model_forecast(model, forecast_series, window_size, batch_size)
```
```{python}
results = forecast.squeeze()
results
```
```{python}
# Reduce the original series
forecast_series = series[split_time-window_size:-1]
# Use helper function to generate predictions
forecast = model_forecast(model, forecast_series, window_size, batch_size)
# Drop single dimensional axis
results = forecast.squeeze()
# Plot the results
plot_series(time_valid, (x_valid, results))
```
## model result
```{python}
## Compute the MAE and MSE
print(tf.keras.metrics.mean_squared_error(x_valid, results).numpy())
```
```{python}
print(tf.keras.metrics.mean_absolute_error(x_valid, results).numpy())
```
# RNN model
## define RNN Model
```{python}
# Build the Model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv1D(filters=64, kernel_size=3,
strides=1,
activation="relu",
padding='causal',
input_shape=[window_size, 1]),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, return_sequences=True),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),
tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 400)
])
# Print the model summary
model.summary()
```
## Tune the Learning Rate
```{python}
# Get initial weights
init_weights = model.get_weights()
```
```{python}
#| error: false
# Set the learning rate scheduler
lr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(
lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))
# Initialize the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(), optimizer=optimizer)
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule],verbose=0)
```
```{python}
# Define the learning rate array
lrs = 1e-8 * (10 ** (np.arange(100) / 20))
# Set the figure size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Set the grid
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the loss in log scale
plt.semilogx(lrs, history.history["loss"])
# Increase the tickmarks size
plt.tick_params('both', length=10, width=1, which='both')
# Set the plot boundaries
plt.axis([1e-8, 1e-3, 0, 100])
```
## define RNN model after tunned
```{python}
# Reset states generated by Keras
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# Reset the weights
model.set_weights(init_weights)
```
```{python}
model.summary()
```
## complie model
```{python}
# Set the learning rate
learning_rate = 8e-7
# Set the optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate, momentum=0.9)
# Set the training parameters
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(),
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=["mae"])
```
## train RNN Model after tunned
```{python}
#| error: false
# Train the model
history = model.fit(train_set,epochs=100,verbose=0)
```
```{python}
# Get mae and loss from history log
mae=history.history['mae']
loss=history.history['loss']
# Get number of epochs
epochs=range(len(loss))
# Plot mae and loss
plot_series(
x=epochs,
y=(mae, loss),
title='MAE and Loss',
xlabel='MAE',
ylabel='Loss',
legend=['MAE', 'Loss']
)
# Only plot the last 80% of the epochs
zoom_split = int(epochs[-1] * 0.2)
epochs_zoom = epochs[zoom_split:]
mae_zoom = mae[zoom_split:]
loss_zoom = loss[zoom_split:]
# Plot zoomed mae and loss
plot_series(
x=epochs_zoom,
y=(mae_zoom, loss_zoom),
title='MAE and Loss',
xlabel='MAE',
ylabel='Loss',
legend=['MAE', 'Loss']
)
```
## Model Prediction
```{python}
# Reduce the original series
forecast_series = series[split_time-window_size:-1]
# Use helper function to generate predictions
forecast = model_forecast(model, forecast_series, window_size, batch_size)
# Drop single dimensional axis
results = forecast.squeeze()
# Plot the results
plot_series(time_valid, (x_valid, results))
```
## model result
```{python}
## Compute the MAE and MSE
print(tf.keras.metrics.mean_squared_error(x_valid, results).numpy())
```
```{python}
print(tf.keras.metrics.mean_absolute_error(x_valid, results).numpy())
```
# save model
```{python}
from keras.models import load_model, save_model
save_model(model,'c4week4sunsports_model.keras')
```
# load model
```{python}
new_model = load_model('c4week4sunsports_model.keras',safe_mode=False )
```
```{python}
new_model.predict(series[0:20][np.newaxis])
```
# resource:
https://www.coursera.org/learn/tensorflow-sequences-time-series-and-prediction
https://github.com/https-deeplearning-ai/tensorflow-1-public/tree/main/C4